Termin-8 Presentation (Poultry)
FEED IS YOUR LARGEST INVESTMENT... Safeguard it with Protecting feed ingredients and finished feed against bacterial and viral contamination Explore Now
Visualizing Risk of Feed Source Pathogens Independent research confirms feed as a fomite for bacterial pathogens such as Salmonella and viral pathogens such as HPAI. Transmission risk varies across the production chain, dependent on the raw materials used, environmental conditions faced and the presence of legacy bacteria in feed and feed ingredient production systems. It’s easy to see why a single-step intervention, without proper recontamination protection, fails to reliably address the challenge. Cropping Ingredient processing/logistics Milling (storage, grinding, mixing, pelleting and cooling) On-farm & in feeders Food processing Profiling based on raw material risk (Richardson et al 2000, legacy bacteria in feed milling (Gosling et al 2022), on farm (Alali and Ricke 2012) and in food processing (EFSA 2022)
A healthy microbiota: 85% 15% beneficial, pathogenic gram-positive bacteria bacteria Gut Health Benefits of Microbiota to Harmful Effects of the Host Microbiota is More than a Microbiota metabolizes SCFA, enzymes, Gut Instinct amino acids, and many B vitamins Microbes compete with host for nutrients SCFA stimulate gut epithelial cell Decrease fat digestibility by proliferation and increase villus height deconjugating bile acids (De Vadder et al, 2014 (Gaskin, 2001) Can produce toxic compounds (ammonia, Competitive exclusion of pathogenic amines, phenols, cresol, indoles) bacteria once established (Klis et al, 2002) Microbiota accelerates turnover rates of Maintains immune homeostasis by enterocytes and goblet cells leading to preventing inflammation high rates of metabolism and protein (Lei et al, 2015) synthesis (Summers, 1991; Cant et al, 1996)
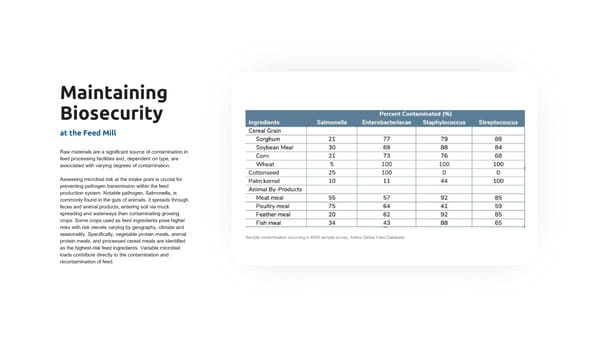
Maintaining Biosecurity at the Feed Mill Raw materials are a significant source of contamination in feed processing facilities and, dependent on type, are associated with varying degrees of contamination. Assessing microbial risk at the intake point is crucial for preventing pathogen transmission within the feed production system. Notable pathogen, Salmonella, is commonly found in the guts of animals. It spreads through feces and animal products, entering soil via muck spreading and waterways then contaminating growing crops. Some crops used as feed ingredients pose higher risks with risk olevels varying by geography, climate and seasonality. Specifically, vegetable protein meals, animal Sample contamination occurring in 8000 sample survey, Anitox Global Feed Database protein meals, and processed cereal meals are identified as the highest-risk feed ingredients. Variable microbial loads contribute directly to the contamination and recontamination of feed.
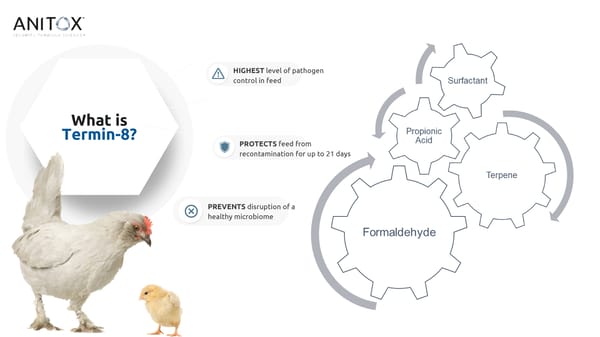
HIGHEST level of pathogen control in feed What is Termin-8? PROTECTS feed from recontamination for up to 21 days PREVENTS disruption of a healthy microbiome
Uniform Termin-8 is a application synergistic blend Surfactant and terpene within the Broad spectrum Each ingredient enhances the formulation aid in the uniform control efficacy of its counterparts. application and disruption of cellular walls. Formaldehyde and Synergism within the formulations propionic acid interrupt critical gives Termin-8 broad spectrum cellular function leading to cell control against molds, yeast and death. bacteria.
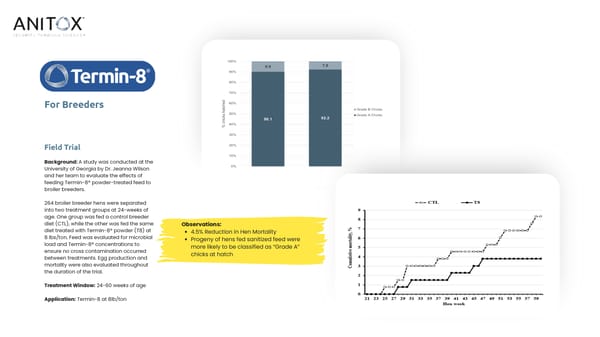
For Breeders Field Trial Background: A study was conducted at the University of Georgia by Dr. Jeanna Wilson and her team to evaluate the effects of feeding Termin-8® powder-treated feed to broiler breeders. 264 broiler breeder hens were separated into two treatment groups at 24-weeks of age. One group was fed a control breeder diet (CTL), while the other was fed the same Observations: diet treated with Termin-8® powder (T8) at 4.5% Reduction in Hen Mortality 8 lbs/ton. Feed was evaluated for microbial Progeny of hens fed sanitized feed were load and Termin-8® concentrations to more likely to be classified as “Grade A” ensure no cross contamination occurred chicks at hatch between treatments. Egg production and mortality were also evaluated throughout the duration of the trial. Treatment Window: 24-60 weeks of age Application: Termin-8 at 8lb/ton
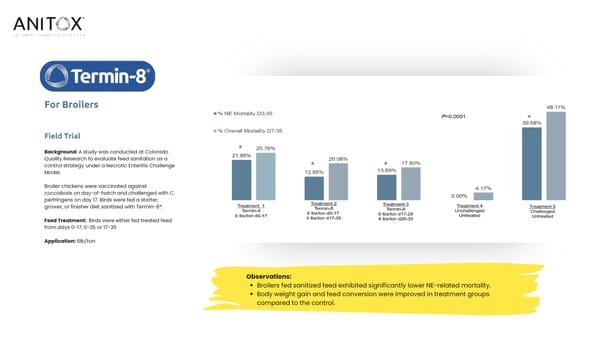
For Broilers Field Trial Background: A study was conducted at Colorado Quality Research to evaluate feed sanitation as a control strategy under a Necrotic Enteritis Challenge Model. Broiler chickens were vaccinated against coccidiosis on day-of-hatch and challenged with C. perfringens on day 17. Birds were fed a starter, grower, or finisher diet sanitized with Termin-8®. Feed Treatment: Birds were either fed treated feed from days 0-17, 0-35 or 17-35 Application: 6lb/ton Observations: Broilers fed sanitized feed exhibited significantly lower NE-related mortality. Body weight gain and feed conversion were improved in treatment groups compared to the control.
87% pullet uniformity For Layers Additional 15 eggs/hen housed Field Trial Mortality reduced by 3% Background: A commercial layer farm in the US with 5,000,000 birds in 3 separate locations initially started a treatment regime for biosecurity purposes at one of its sites. They quickly identified significant performance advantages in the replacement pullet flock receiving treated feed when compared to others. Treatment Window: 1-17 weeks Application: 6lb/ton Observations: Uniformity of the treated flock was improved, resulting in an on time start of egg laying compared with sister flocks which were delayed. Birds receiving treated feed also demonstrated improved visible health (comb color), and reduction in incidence of diarrhea. Necropsy showed fewer signs of enteritis.
FCR improved by 15 points For Turkey Producers Average daily gain increased by 12% Field Trial Mortality reduced by 1.3% Background: An integrated turkey producer in the USA observed poor poult performance in the first 14 days. Upon necropsy, they saw underdeveloped intestines with thin walls and short villi and ballooned ceca. While poults seemed to recover, average body weight and FCR continued to lag. Initially, the producer gave antibiotic treatment in a single house and saw improved performance. However, due to their organic certification, this was not a viable solution. Pre-starter feed samples had high total bacteria, with some samples testing positive for Clostridia and Salmonella. The producer performed a field trial to determine the impact of Termin-8® treated feed on poult mortality in the first 14 days. Trial Duration: 1-21 Days Application: 6lb/ton Observations: Poults fed Termin-8® treated feed had improved body weights, average daily gain, FCR and reduced mortality.